| |
MaskingThe sink coding part of the MPEG audio encoder is realized through taking into account masking phenomena [14,15,19]. Masking occurs if two or more simultaneous tonal or narrowband noise components are close to each other in frequency domain. Weaker components are masked by stronger components due to local elevation of the hearing threshold - those parts that fall below the modified threshold are effectively too weak to invoke any auditory sensation (they become inaudible). 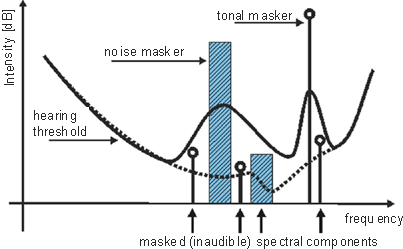 Modification of the hearing threshold due to the presence of strong components masking other components Masking is also observed for non-simultaneous stimuli. Post-masking is particularly significant if a weaker sound follows a strong masker within a period of 0...200 ms.
|